| How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank. |
|
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
|
CCNAv7 ENSA Skills Assessment – ENSA Final Skills Exam (Equipment)
Your exam may be different
Topology
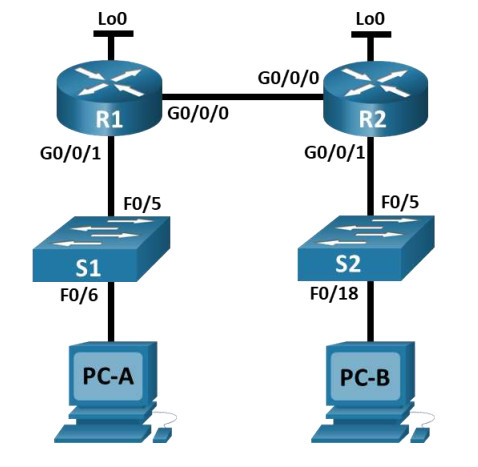
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 10.67.254.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| Lo0 | 10.52.0.1 | 255.255.255.248 | N/A | |
| R2 | G0/0/0 | 10.67.254.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| Lo0 | 209.165.201.1 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A | |
| G0/0/1 | 10.67.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| S2 | VLAN 1 | 10.67.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.67.1.1 |
Assessment Objectives
- Part 1: Initialize, Reload and Configure Basic Device Settings (40 points, 40 minutes)
- Part 2: Configure and Single Area OSPFv2 (20 points, 10 minutes)
- Part 3: Optimize Single Area OSPFv2 (25 points, 20 minutes)
- Part 4: Configure Access Control, NAT, and perform configuration backup (15 points, 30 minutes)
Scenario
In this Skills Assessment (SA) you will configure the devices in a small network. You must configure a router, switch and PCs to support IPv4 connectivity for supported hosts. Your router and switch must also be managed securely. You will configure Single-Area OSPFv2, NAT, and access control lists. Further, you will backup up your working configurations to a TFTP server.
Required Resources
- 2 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 2 PCs (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Initialize, Reload and Configure Basic Device Settings
Total points: 40
Time: 40 minutes
Step 1: Initialize and reload routers and switches.
Erase the startup configurations and VLANs from the router and switch and reload the devices.
Before proceeding, ask your instructor verify device initializations.
On Router R1-R2
Router>enable Router#erase startup-config Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm] [OK] Erase of nvram: complete %SYS-7-NV_BLOCK_INIT: Initialized the geometry of nvram Router#reload
On Switch S1-S2
Switch>enable Switch#erase startup-config Switch#delete vlan.dat Delete filename [vlan.dat]? Delete flash:/vlan.dat? [confirm] Switch#reload
Step 2: Configure the routers.
Configuration tasks for R1 and R2 include the following:
| Task | Specification | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disable DNS lookup | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Router name | R1 or R2, as appropriate | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Domain name | ccna-lab.com | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Encrypted privileged EXEC password | ciscoenpass | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Console access password | ciscoconpass | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Set the minimum length for passwords | 10 characters | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Create an administrative user in the local database | Username: admin Password: admin1pass | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Set login on VTY lines to use local database | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Set VTY lines to accept SSH connections only | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Encrypt the clear text passwords | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Configure an MOTD Banner | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Configure interface G0/0/1 | Set the description Set the Layer 3 IPv4 address Activate Interface | 2 pts | 2 pts |
| Configure interface G0/0/0 | Set the description Set the Layer 3 IPv4 address Activate Interface | 2 pts | 2 pts |
| Configure interface Lo0 | Configure IPv4 address | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pts |
| Generate an RSA crypto key | 1024 bits modulus | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
R1
Router>enable Router#config terminal Router(config)#no ip domain lookup Router(config)#hostname R1 R1(config)#ip domain-name ccna-lab.com R1(config)#enable secret ciscoenpass R1(config)#line console 0 R1(config-line)#password ciscoconpass R1(config-line)#login R1(config-line)#exit R1(config)#security passwords min-length 10 R1(config)#username admin secret admin1pass R1(config)#line vty 0 15 R1(config-line)#login local R1(config-line)#transport input ssh R1(config-line)#exit R1(config)#service password-encryption R1(config)#banner motd #Unauthorized Access is Prohibited# R1(config)#interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)#description Connect to R2 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.67.254.2 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)#description Connect to LAN A R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)##interface loopback 0 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.52.0.1 255.255.255.248 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#crypto key generate rsa How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024 R1(config)#
R2
Router>enable Router#config terminal Router(config)#no ip domain lookup Router(config)#hostname R2 R2(config)#ip domain-name ccna-lab.com R2(config)#enable secret ciscoenpass R2(config)#line console 0 R2(config-line)#password ciscoconpass R2(config-line)#login R2(config-line)#exit R2(config)#security passwords min-length 10 R2(config)#username admin secret admin1pass R2(config)#line vty 0 15 R2(config-line)#login local R2(config-line)#transport input ssh R2(config-line)#exit R2(config)#service password-encryption R2(config)#banner motd #Unauthorized Access is Prohibited# R2(config)#interface g0/0/0 R2(config-if)#description Connect to R1 R2(config-if)#ip address 10.67.254.1 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#interface g0/0/1 R2(config-if)#description Connect to LAN B R2(config-if)#ip address 10.67.1.1 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)##interface loopback 0 R2(config-if)#ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224 R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#crypto key generate rsa How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024 R2(config)#
Step 3: Configure S1 and S2.
Configuration tasks for the switches include the following:
| Task | Specification | S1 | S2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disable DNS lookup | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Switch name | S1 or S2, as appropriate | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Domain name | ccna-lab.com | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Encrypted privileged EXEC password | ciscoenpass | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Console access password | ciscoconpass | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Shutdown all unused interfaces | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Create an administrative user in the local database | Username: admin Password: admin1pass | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Set login on VTY lines to use local database | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Set VTY lines to accept SSH connections only | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Encrypt the clear text passwords | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Configure an MOTD Banner | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt | |
| Generate an RSA crypto key | 1024 bits modulus | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Configure Management Interface (SVI) for VLAN 1 (the Management VLAN) | Set the Layer 3 IPv4 address | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
| Configure Default Gateway | 0.5 pt | 0.5 pt |
S1
Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#no ip domain-lookup Switch(config)#hostname S1 S1(config)#ip domain-name ccna-lab.com S1(config)#enable secret ciscoenpass S1(config)#line console 0 S1(config-line)#password ciscoconpass S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#exit S1(config)#interface range f0/1-4, f0/7-24, g0/1-2 S1(config-if-range)#shutdown S1(config-if-range)#exit S1(config)#username admin secret admin1pass S1(config)#line vty 0 15 S1(config-line)#login local S1(config-line)#transport input ssh S1(config-line)#exit S1(config)#service password-encryption S1(config)#banner motd #Unauthorized access or use prohibited# S1(config)#crypto key generate rsa How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024 S1(config)# interface vlan 1 S1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)#no shutdown S1(config-if)#exit S1(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
S2
Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#no ip domain-lookup Switch(config)#hostname S2 S2(config)#ip domain-name ccna-lab.com S2(config)#enable secret ciscoenpass S2(config)#line console 0 S2(config-line)#password ciscoconpass S2(config-line)#login S2(config-line)#exit S2(config)#interface range f0/1-4, f0/6-17, f0/19-24, g0/1-2 S2(config-if-range)#shutdown S2(config-if-range)#exit S2(config)#username admin secret admin1pass S2(config)#line vty 0 15 S2(config-line)#login local S2(config-line)#transport input ssh S2(config-line)#exit S2(config)#service password-encryption S2(config)#banner motd #Unauthorized access or use prohibited# S2(config)#crypto key generate rsa How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024 S2(config)# interface vlan 1 S2(config-if)#ip address 10.67.1.2 255.255.255.0 S2(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config-if)#exit S2(config)#ip default-gateway 10.67.1.1
Points for Step 1 (5 points):
Enter score here.
Points for Step 2 (21 points):
Enter score here.
Points for Step 3 (14 points):
Enter score here.
Instructor Sign-off Part 1:
Instructor Sign-off
Total points for Part 1 (40 points):
Enter score here.
Part 2: Configure Single Area OSPFv2
Total points: 10
Time: 10 minutes
Configuration tasks for R1 and R2 include the following:
| Task | Specification | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configure the OSPF routing process | Use process id 1 | 1 pt | 1 pt |
| Manually configure the router id | Use 0.0.0.1 for R1 and 0.0.0.2 for R2 | 1 pt | 1 pt |
| Configure network statements | Configure a network statement for each locally attached network using a wild card mask that matches each network’s subnet mask Note: R2 Lo0 network should not be included in the OSPF process. | 3 pts | 3 pts |
R1
User Access Verification Password: ciscoconpass R1>enable Password: ciscoenpass R1#configure terminal R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 R1(config-router)#network 10.67.254.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R1(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)#network 10.52.0.0 0.0.0.7 area 0 R1(config-router)#
User Access Verification Password: ciscoconpass R2>enable Password: ciscoenpass R2#configure terminal R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.2 R2(config-router)#network 10.67.254.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)#network 10.67.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R2(config-router)#
Instructor Sign-off Part 2
Instruction Sign-off
Total Points (10 points):
Enter score here.
Part 3: Optimize Single-Area OSPFv2
Total points: 20
Time: 20 minutes
Step 1: Configure R1.
Configuration Tasks for R1 include the following:
| Task | Specification | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Configure passive interfaces | Configure all interfaces that are not directly connected to an OSPF neighbor to be passive | 3 points |
| Configure the reference bandwidth | Adjust the reference bandwidth to 1 Gigabit | 2 points |
| Configure Loopback 0 to report the mask it is configured with instead of a host mask | Configure Loopback0 as a point-to-point network for OSPF | 2 points |
| Tune the timers for your network | Configure the hello time for 30 seconds | 1 point |
Router 1
R1>enable
Password: ciscoenpass
R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#passive-interface g0/0/1
R1(config-router)#passive-interface loopback 0
R1(config-router)#auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#interface loopback 0
R1(config-if)#ip ospf network point-to-point
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface g0/0/0
R1(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 30
R1(config-if)#Step 2: Configure R2.
Configuration tasks for R2 include the following:
| Task | Specification | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Configure passive interfaces | Configure all interfaces that are not directly connected to an OSPF neighbor to be passive | 2 points |
| Configure the reference bandwidth | Adjust the reference bandwidth to 1 Gigabit | 2 points |
| Provide default routing for the OSPF domain | Configure a static default route with loopback 0 as the exit interface, then share the default information with other OSPF speakers | 5 points |
| Tune the timers for your network | Configure the hello time for 30 seconds | 1 point |
| Tune the DR/BDR election to favor R2 | Set the OSPF priority for R2 to a value of 50 | 2 points |
Router 2
R2>en
Password: ciscoenpass
R2#configure terminal
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#passive-interface g0/0/1
R2(config-router)#passive-interface loopback 0
R2(config-router)#auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 loopback 0
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#default-information originate
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#interface g0/0/0
R2(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 30
R2(config-if)#ip ospf priority 50
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#Points for Step 1 (8 points)
Enter score here.
Points for Step 2 (12 points)
Enter score here.
Instructor Sign-off Part 3:
Instructor Sign-off
Total points (20 points):
Enter score here.
Part 4: Configure Access Control, NAT, and perform configuration backup
Total points: 30
Time: 30 minutes
Step 1: Configure host computers.
Configure the host computers PC-A and PC-B with IPv4 addresses. (4 points)
| Description | PC-A | PC-B |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address | 192.168.1.50 | 10.67.1.50 |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.0 | 255.255.255.0 |
| Default Gateway | 192.168.1.1 | 10.67.1.1 |
PC-A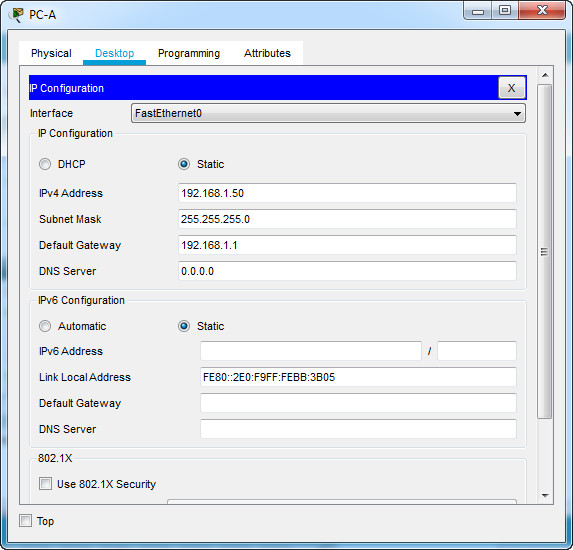
PC-B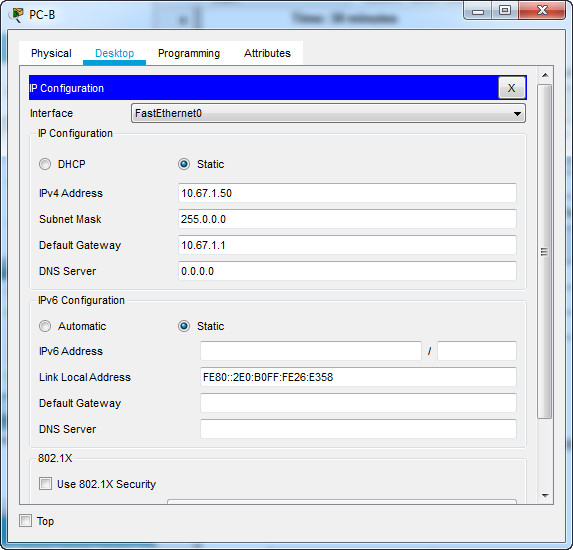
After configuring each host computer, perform the following tests: (4 points)
| Source | Target | Protocol | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC-A | PC-B | Ping (C:\>ping 10.67.1.50) | Success |
| PC-A | https://209.165.201.1 | HTTPS (On browser, access: https://209.165.201.1) | Success |
| PC-A | 209.165.201.1 | SSH C:\>ssh -l admin 209.165.201.1 Enter password: admin1pass | Success |
| PC-B | 209.165.201.1 | SSH C:\>ssh -l admin 209.165.201.1 Enter password: admin1pass | Success |
If you get different results, troubleshoot your OSPF and host configurations.
Note: If you are unable to access 209.165.201.1 via https, enter ip http secure-server at R2 CLI.
R2(config)# ip http secure-server
Step 2: Configure Access Control on R2.
Create and apply an access control list on R2 named R2-SECURITY to do the following:
| Task | Specification | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Create an access control list | R2-SECURITY | 2 points |
| Control HTTP and HTTPS traffic | Only hosts from the 10.0.0.0/8 network are allowed to reach the web server at 209.165.201.1 | 2 points |
| Control SSH traffic | SSH is not allowed to the address 209.165.201.1 | 2 points |
| Permit traffic | All other traffic, regardless of protocol, is allowed | 2 points |
| Apply the ACL | Filter traffic originating from R1 | 2 points |
On Router R2
R2(config)#ip access-list extended R2-SECURITY R2(config-ext-nacl)#deny tcp any host 209.165.201.1 eq 443 R2(config-ext-nacl)#deny tcp any host 209.165.201.1 eq 22 R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip any any R2(config-ext-nacl)#exit R2(config)#interface g0/0/0 R2(config-if)#ip access-group R2-SECURITY in
After configuring and applying the ACL, perform the following tests: (2 points)
| Source | Target | Protocol | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC-A | PC-B | Ping | Success |
| PC-A | https://209.165.201.1 | HTTPS | Failure |
| PC-A | 209.165.201.1 | SSH | Failure |
| PC-B | 209.165.201.1 | SSH | Success |
If you get different results, double check your ACL configuration and application.
Step 3: Configure NAT.
The decision has been made that the entire organization should be using addresses in the 10.0.0.0/8 network space. R1’s LAN is out of compliance. There are applications and services running in the R1 LAN that cannot have their IP address changed without the entire system being rebuilt, so NAT is in order. Here are the configuration tasks at R1:
| Task | Specification | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Remove 192.168.1.0/24 from OSPF | Remove the appropriate network statement at R1 | 2 points |
| Create an ACL to identify hosts allowed to be translated | Create an ACL that matches the 192.168.1.0 network | 2 points |
| Configure Port Address Translation on the outside interface of R1 | Configure the NAT association between the ACL and the interface g0/0/0 so that it uses port address translation | 2 points |
| Identify the interfaces involved in NAT | Specify inside or outside on the appropriate interfaces | 2 points |
On Router R1
R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#no network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)#exit R1(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 R1(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 interface g0/0/0 overload R1(config)#interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ip nat outside R1(config-if)#interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)#ip nat inside R1(config-if)#
Step 4: Backup all device configurations.
| Task | Specification | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Using the TFTP server on PC-B, backup the running configuration of all of your devices to PC-B using the TFTP protocol | 2 points |
On 4 devices: R1, R2, S1, S2:
User Access Verification Password: ciscoconpass R1/R2/S1/S2>en Password: ciscoenpass R1/R2/S1/S2#copy running-config tftp Address or name of remote host []? 10.67.1.50
If you are testing on a real device, you can install and use SolarwinTFTP on PC-B as TFTP server
Points for Step 1 (8 points):
Enter score here.
Points for Step 2 (12 points):
Enter score here.
Points for Step 3 (8 points):
Enter score here.
Points for Step 4 (2 points):
Enter score here.
Instructor Sign-off Part 4:
Instructor Sign-off
Total points (30 points):
Enter score here.
Part 5: Cleanup
NOTE: DO NOT PROCEED WITH CLEANUP UNTIL YOUR INSTRUCTOR HAS GRADED YOUR SKILLS EXAM AND HAS INFORMED YOU THAT YOU MAY BEGIN CLEANUP.
Unless directed otherwise by the instructor, restore host computer network connectivity, and then turn off power to the host computers.
Before turning off power to the router and switch, remove the NVRAM configuration files (if saved) from both devices.
Disconnect and neatly put away all LAN cables that were used in the Final.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device.
The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.