| How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank. |
|
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
|
Network Security (Version 1.0) Practice Final Answers
1. Which two statements are true about ASA standard ACLs? (Choose two.)
- They identify only the destination IP address.
- They are the most common type of ACL.
- They are applied to interfaces to control traffic.
- They specify both the source and destination MAC address.
- They are typically only used for OSPF routes.
Explanation: ASA standard ACLs are used to identify the destination IP addresses, unlike IOS ACLs where a standard ACL identifies the source host/network. They are typically only used for OSPF routes and can be used in a route map for OSPF redistribution. Standard access lists cannot be applied to interfaces to control traffic.
2. When dynamic NAT on an ASA is being configured, what two parameters must be specified by network objects? (Choose two.)
- the inside NAT interface
- the interface security level
- the outside NAT interface
- a range of private addresses that will be translated
- the pool of public global addresses
Explanation: On an ASA, both the pool of addresses that will be used as inside global address and the range of internal private addresses that should be translated are configured through network objects.
3. Which protocol uses X.509 certificates to support mail protection performed by mail agents?
- IPsec
- SSL
- S/MIME
- EAP-TLS
Explanation: Many applications use the X.509 standard format of digital certificates to authenticate websites, public key distribution, and end devices connected to switch ports. User email agents use the S/MIME protocol to support email protection. S/MIME uses X.509 certificates.
4. What are two security features commonly found in a WAN design? (Choose two.)
- WPA2 for data encryption of all data between sites
- firewalls protecting the main and remote sites
- outside perimeter security including continuous video surveillance
- port security on all user-facing ports
- VPNs used by mobile workers between sites
Explanation: WANs span a wide area and commonly have connections from a main site to remote sites including a branch office, regional site, SOHO sites, and mobile workers. WANs typically connect over a public internet connection. Each site commonly has a firewall and VPNs used by remote workers between sites.
5. What is an appropriate use for class 5 digital certificates?
- used for online business transactions between companies
- used for private organizations or government security
- used by organizations for which proof of identity is required
- used for testing in situations in which no checks have been performed
Explanation: The CA class number determines how rigorous the procedure was that verified the identity of the holder when the certificate was issued. The higher the class number, the more trusted the certificate. Class numbers range from 0 to 5. A class 5 certificate is the most trusted, and class 0 the least trusted. Class 5 is used for private organizations or government security.
6. Which two statements are characteristics of a virus? (Choose two.)
- A virus typically requires end-user activation.
- A virus has an enabling vulnerability, a propagation mechanism, and a payload.
- A virus replicates itself by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks.
- A virus provides the attacker with sensitive data, such as passwords.
- A virus can be dormant and then activate at a specific time or date.
Explanation: The type of end user interaction required to launch a virus is typically opening an application, opening a web page, or powering on the computer. Once activated, a virus may infect other files located on the computer or other computers on the same network.
7. Match the information security component with the description.
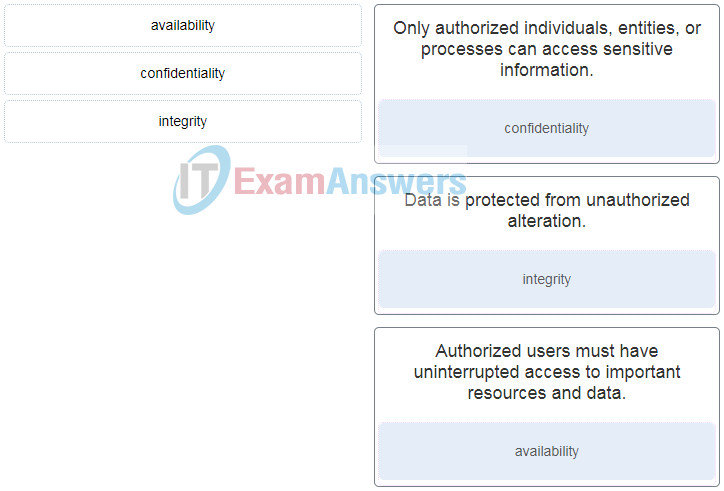
8. Match the security policy with the description. (Not all options are used.)
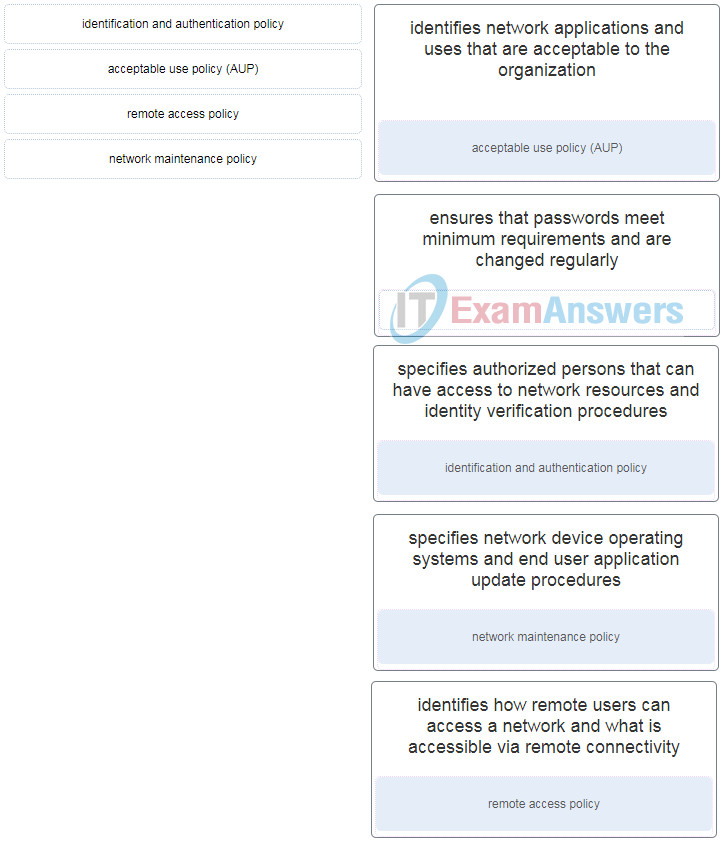
9. How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
- It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
- It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.
- It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
- It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
Explanation: The service password-encryption command encrypts plaintext passwords in the configuration file so that they cannot be viewed by unauthorized users.
10. Which benefit does SSH offer over Telnet for remotely managing a router?
- encryption
- TCP usage
- authorization
- connections via multiple VTY lines
Explanation: SSH provides secure access to a network device for remote management. It uses a stronger password authorization than Telnet does and encrypts any data that is transported during the session.
11. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the JR-Admin account is true?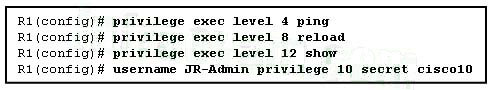
- JR-Admin can issue show , ping , and reload commands.
- JR-Admin can issue ping and reload commands.
- JR-Admin can issue only ping commands.
- JR-Admin can issue debug and reload commands.
- JR-Admin cannot issue any command because the privilege level does not match one of those defined.
Explanation: When the username name privilege 10 command is issued, access to commands with a privilege level of 10 or less (0-10) is permitted to the user.
12. What protocol is used by SCP for secure transport?
- IPSec
- HTTPS
- SSH
- Telnet
- TFTP
Explanation: The Secure Copy (SCP) feature provides a secure and authenticated method for copying and saving router configuration files by using SSH.
13. Refer to the exhibit. What type of syslog message is displayed?
- warning
- notification
- informational
- debugging
Explanation: The severity level is used to provide an explanation for the event or error that is occurring within the Cisco IOS. The smaller the number of the severity level, the more critical the event. A Syslog message with a level 5 is considered a notification message.
14. What command must be issued on a Cisco router that will serve as an authoritative NTP server?
- ntp master 1
- ntp server 172.16.0.1
- ntp broadcast client
- clock set 11:00:00 DEC 20 2010
Explanation: Routers that will serve as NTP masters must be configured with the ntp master command. A client is configured with the ntp server command so that the client can locate the NTP master. The ntp broadcast client command allows NTP to use to broadcast messages. The clock set command is used to set the time on a router.
15. A server log includes this entry: User student accessed host server ABC using Telnet yesterday for 10 minutes. What type of log entry is this?
- authentication
- authorization
- accounting
- accessing
Explanation: Accounting records what users do and when they do it, including what is accessed, the amount of time the resource is accessed, and any changes that were made. Accounting keeps track of how network resources are used.
16. Which three types of views are available when configuring the role-based CLI access feature? (Choose three.)
- superuser view
- root view
- superview
- CLI view
- admin view
- config view
Explanation: There are three types of Role-based CLI views:
1) root view
2) CLI view
3) superview
17. What is the purpose of using the ip ospf message-digest-key key md5 password command and the area area-id authentication message-digest command on a router?
- to encrypt OSPF routing updates
- to enable OSPF MD5 authentication on a per-interface basis
- to configure OSPF MD5 authentication globally on the router
- to facilitate the establishment of neighbor adjacencies
Explanation: To configure OSPF MD5 authentication globally, the ip ospf message-digest-key key md5 password interface configuration command and the area area-id authentication message-digest router configuration command are issued. To configure OSPF MD5 authentication per interface, the ip ospf message-digest-key key md5 password interface configuration command and the ip ospf authentication message-digest interface configuration command are issued. Authentication does not encrypt OSPF routing updates. The requirements to establish OSPF router neighbor adjacencies are separate from authentication.
18. What is indicated by the use of the local-case keyword in a local AAA authentication configuration command sequence?
- that user access is limited to vty terminal lines
- that passwords and usernames are case-sensitive
- that AAA is enabled globally on the router
- that a default local database AAA authentication is applied to all lines
Explanation: The use of the local-case keyword means that the authentication is case-sensitive. It does not enable or apply the AAA configuration to router interfaces or lines.
19. A network administrator is configuring an AAA server to manage RADIUS authentication. Which two features are included in RADIUS authentication? (Choose two.)
- encryption for all communication
- hidden passwords during transmission
- single process for authentication and authorization
- separate processes for authentication and authorization
- encryption for only the data
Explanation: RADIUS authentication supports the following features:RADIUS authentication and authorization as one process
Encrypts only the password
Utilizes UDP
Supports remote-access technologies, 802.1X, and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
20. A network administrator is explaining to a junior colleague the use of the lt and gt keywords when filtering packets using an extended ACL. Where would the lt or gt keywords be used?
- in an IPv6 extended ACL that stops packets going to one specific destination VLAN
- in an IPv4 named standard ACL that has specific UDP protocols that are allowed to be used on a specific server
- in an IPv6 named ACL that permits FTP traffic from one particular LAN getting to another LAN
- in an IPv4 extended ACL that allows packets from a range of TCP ports destined for a specific network device
Explanation: The lt and gt keywords are used for defining a range of port numbers that are less than a particular port number or greater than a particular port number.
21. Which feature is unique to IPv6 ACLs when compared to those of IPv4 ACLs?
- the use of wildcard masks
- an implicit deny any any statement
- the use of named ACL statements
- an implicit permit of neighbor discovery packets
Explanation: One of the major differences between IPv6 and IPv4 ACLs are two implicit permit statements at the end of any IPv6 ACL. These two permit statements allow neighbor discovery operations to function on the router interface.
22. Refer to the exhibit. An extended access list has been created to prevent human resource users from gaining access to the accounting server. All other network traffic is to be permitted. When following the ACL configuration guidelines, on which router, interface, and direction should the access list be applied?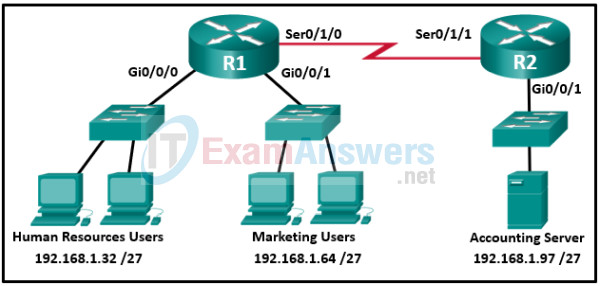
- router R1, interface S0/1/0, outbound
- router R2, interface Gi0/0/1, outbound
- router R2, interface Gi0/0/1, inbound
- router R1, interface Gi0/0/0, inbound
- router R2, interface S0/1/1, inbound
- router R1, interface Gi0/0/0, outbound
Explanation: The ACL configuration guidelines recommend placing extended access control lists as close to the source of network traffic as possible and placing standard access control lists as close to the destination of network traffic as possible.
23. Which statement describes the characteristics of packet-filtering and stateful firewalls as they relate to the OSI model?
- Both stateful and packet-filtering firewalls can filter at the application layer.
- A stateful firewall can filter application layer information, whereas a packet-filtering firewall cannot filter beyond the network layer.
- A packet-filtering firewall typically can filter up to the transport layer, whereas a stateful firewall can filter up to the session layer.
- A packet-filtering firewall uses session layer information to track the state of a connection, whereas a stateful firewall uses application layer information to track the state of a connection.
Explanation: Packet filtering firewalls can always filter Layer 3 content and sometimes TCP and UDP-based content. Stateful firewalls monitor connections and thus have to be able to support up to the session layer of the OSI model.
24. Which special hardware module, when integrated into ASA, provides advanced IPS features?
- Content Security and Control (CSC)
- Advanced Inspection and Prevention (AIP)
- Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Card (AIP-SSC)
- Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Module (AIP-SSM)
Explanation: The advanced threat control and containment services of an ASA firewall are provided by integrating special hardware modules with the ASA architecture. These special modules include:
Advanced Inspection and Prevention (AIP) module – supports advanced IPS capability.
Content Security and Control (CSC) module – supports antimalware capabilities.
Cisco Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Module (AIP-SSM) and Cisco Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Card (AIP-SSC) – support protection against tens of thousands of known exploits.
25. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring the security level for the ASA. What is a best practice for assigning the security level on the three interfaces?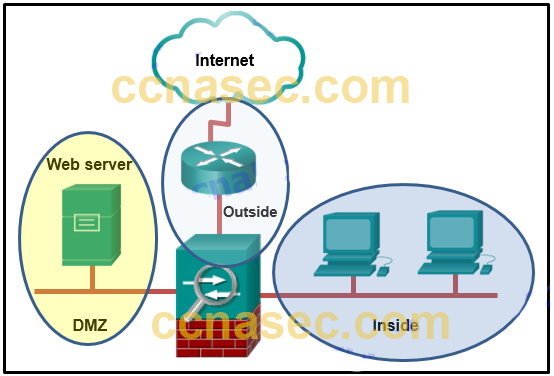
- Outside 0, Inside 35, DMZ 90
- Outside 40, Inside 100, DMZ 0
- Outside 0, Inside 100, DMZ 50
- Outside 100, Inside 10, DMZ 40
Explanation: The Cisco ASA assigns security levels to distinguish among different networks it connects. Security levels define the level of trustworthiness of an interface. The higher the level, the more trusted the interface. The security level numbers range between 0 (untrustworthy) to 100 (very trustworthy). Therefore, the interface connecting to the Internet should be assigned the lowest level. The interface connecting to the internal network should be assigned the highest level. The interface connecting to the DMZ network should be assigned a level between them.
26. What is an advantage in using a packet filtering firewall versus a high-end firewall appliance?
- Packet filters perform almost all the tasks of a high-end firewall at a fraction of the cost.
- Packet filters represent a complete firewall solution.
- Packet filters are not susceptible to IP spoofing.
- Packet filters provide an initial degree of security at the data-link and network layer.
Explanation: There are several advantages of using a packet filtering firewall:
– allows for implementing simple permit or deny rule sets.
– has a low impact on network performance
– is easy to implement, and is supported by most routers
– provides an initial degree of security at the network layer
– performs almost all the tasks of a high-end firewall at a much lower cost
27. Which type of firewall is commonly part of a router firewall and allows or blocks traffic based on Layer 3 and Layer 4 information?
- stateless firewall
- stateful firewall
- proxy firewall
- application gateway firewall
Explanation: A stateless firewall uses a simple policy table look-up that filters traffic based on specific criteria. These firewalls are usually part of a router firewall. They permit or deny traffic based on Layer 3 and Layer 4 information.
28. A company is deploying a new network design in which the border router has three interfaces. Interface Serial0/0/0 connects to the ISP, GigabitEthernet0/0 connects to the DMZ, and GigabitEthernet/01 connects to the internal private network. Which type of traffic would receive the least amount of inspection (have the most freedom of travel)?
- traffic that is going from the private network to the DMZ
- traffic that originates from the public network and that is destined for the DMZ
- traffic that is returning from the DMZ after originating from the private network
- traffic that is returning from the public network after originating from the private network
Explanation: Most traffic within an organization originates from a private IP address. The amount of inspection done to that traffic depends on its destination or whether traffic that is going to that private IP address originated the connection. The demilitarized zone typically holds servers. Traffic that is destined to those servers is filtered based on what services are being provided by the server (HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, etc.).
29. What are two benefits offered by a zone-based policy firewall on a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
- Policies are defined exclusively with ACLs.
- Policies are applied to unidirectional traffic between zones.
- Policies provide scalability because they are easy to read and troubleshoot.
- Any interface can be configured with both a ZPF and an IOS Classic Firewall.
- Virtual and physical interfaces are put in different zones to enhance security.
Explanation: There are several benefits of a ZPF:
It is not dependent on ACLs.
The router security posture is to block unless explicitly allowed.
Policies are easy to read and troubleshoot. This provides scalability because one policy affects any given traffic, instead of needing multiple ACLs and inspection actions for different types of traffic.
Virtual and physical interfaces can be grouped into zones.
Policies are applied to unidirectional traffic between zones.
Both IOS Classic Firewalls and ZPFs can be enabled concurrently on a Cisco router. However, the models cannot be combined on a single interface.
30. When a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall is being configured via CLI, which step must be taken after zones have been created?
- Design the physical infrastructure.
- Establish policies between zones.
- Identify subsets within zones.
- Assign interfaces to zones.
Explanation: The steps for configuring zones in a Zone-Based Policy Firewall are as follows:
– Step 1. Determine the zones.
– Step 2. Establish policies between zones.
– Step 3. Design the physical infrastructure.
– Step 4. Identify subsets within zones and merge traffic requirements.
31. What are two shared characteristics of the IDS and the IPS? (Choose two.)
- Both are deployed as sensors.
- Both analyze copies of network traffic.
- Both use signatures to detect malicious traffic.
- Both have minimal impact on network performance.
- Both rely on an additional network device to respond to malicious traffic.
Explanation: Both the IDS and the IPS are deployed as sensors and use signatures to detect malicious traffic. The IDS analyzes copies of network traffic, which results in minimal impact on network performance. The IDS also relies on an IPS to stop malicious traffic.
32. When a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall is being configured, which two actions can be applied to a traffic class? (Choose two.)
- log
- hold
- drop
- inspect
- copy
- forward
Explanation: The three actions that can be applied are inspect, drop,and pass.
Inspect – This action offers state-based traffic control.
Drop – This is the default action for all traffic. Similar to the implicit deny any at the end of every ACL, there is an explicit drop applied by the IOS to the end of every policy map.
Pass – This action allows the router to forward traffic from one zone to another.
33. Match the network security device type with the description.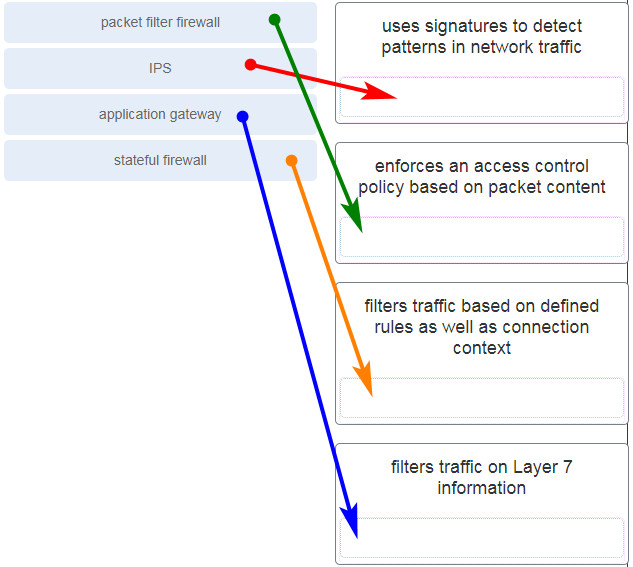
34. What is a characteristic of an IPS atomic signature?
- it can be slow and inefficient to analyze traffic
- it requires several pieces of data to match an attack
- it is a stateful signature
- it is the simplest type of signature
Explanation: There are two types of IPS signatures:
Atomic – This is the simplest type of signature because it does not require the IPS to maintain state information and it can identify an attack with a single packet, activity, or event.
Composite – This is a stateful type of signature. It requires that the IPS maintain state information to match an attack signature.
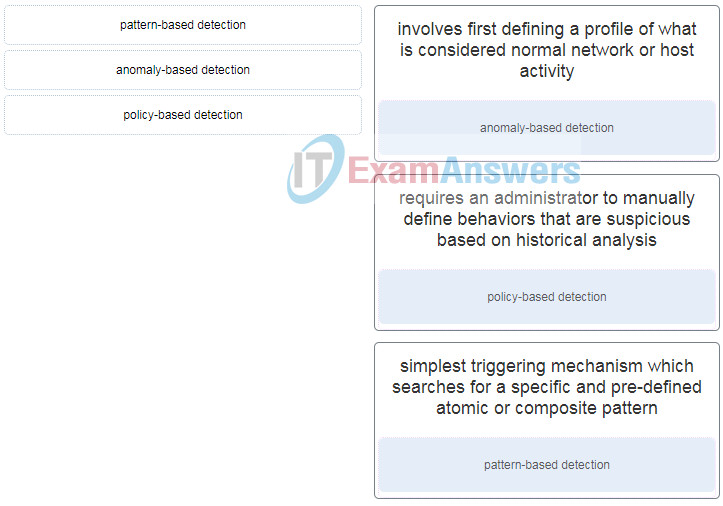
35. Match each IPS signature trigger category with the description.
36. A company is concerned about data theft if any of the corporate laptops are stolen. Which Windows tool would the company use to protect the data on the laptops?
- AMP
- 802.1X
- RADIUS
- BitLocker
Explanation: Storage devices can be encrypted to protect data from unauthorized access. Windows BitLocker provides drive encryption.
37. What protocol is used to encapsulate the EAP data between the authenticator and authentication server performing 802.1X authentication?
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- SSH
- MD5
Explanation: Encapsulation of EAP data between the authenticator and the authentication server is performed using RADIUS.
38. A company requires the use of 802.1X security. What type of traffic can be sent if the authentication port-control auto command is configured, but the client has not yet been authenticated?
- SNMP
- EAPOL
- broadcasts such as ARP
- any data encrypted with 3DES or AES
Explanation: 802.1X prevents unauthorized devices from gaining access to the network. The authentication port-control auto command turns on 802.1X access control. Until the client is authenticated, 802.1X only allows Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPOL), Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) traffic to pass through the port. EAPOL messages are sent between the client and the authenticator such as a switch. If authentication is successful, normal traffic can be sent and received through the port.
39. Which two security features can cause a switch port to become error-disabled? (Choose two.)
- root guard
- PortFast with BPDU guard enabled
- protected ports
- storm control with the trap option
- port security with the shutdown violation mode
Explanation: Error-disabled mode is a way for a switch to automatically shut down a port that is causing problems, and usually requires manual intervention from an administrator to restore the port. When port security is configured to use the shutdown violation mode, it will put the port into the error-disabled mode when the maximum number of MAC addresses is exceeded. Likewise, BPDU guard will put the port into error-disabled mode if a BPDU arrives on a PortFast enabled interface. Storm control will only put the port into the error-disabled mode when configured with the shutdown option. The trap option will simply create an SNMP log message.
40. What are three techniques for mitigating VLAN hopping attacks? (Choose three.)
- Disable DTP.
- Enable trunking manually.
- Set the native VLAN to an unused VLAN.
- Enable BPDU guard.
- Enable Source Guard.
- Use private VLANs.
Explanation: Mitigating a VLAN hopping attack can be done by disabling Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), manually setting ports to trunking mode, and by setting the native VLAN of trunk links to VLANs not in use.
41. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring DAI on switch SW1. What is the result of entering the exhibited commands?
- DAI will validate both source and destination MAC addresses as well as the IP addresses in the order specified. If all parameters are valid then the ARP packet is allowed to pass.
- DAI will validate both source and destination MAC addresses as well as the IP addresses in the order specified. When one set of parameters are valid, the ARP packet is allowed to pass.
- DAI will validate only the destination MAC addresses.
- DAI will validate only the IP addresses.
Explanation: DAI can be configured to check for destination MAC, source MAC, and IP addresses. However, only one ip arp inspection validate command can be configured. Entering multiple ip arp inspection validate commands overwrites the previous command.
42. During a recent pandemic, employees from ABC company were allowed to work from home. What security technology should be implemented to ensure that data communications between the employees and the ABC Head Office network remain confidential?
- a symmetric or asymmetric encryption algorithm such as AES or PKI
- a hashing algorithm such as MD5
- a hash message authentication code such as HMAC
- a hash-generating algorithm such as SHA
Explanation: MD5 and SHA are hash-generating algorithms that guarantee that no one intercepted the message and altered it. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a popular symmetric encryption algorithm where each communicating party needs to know the pre-shared key. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is an asymmetric encryption algorithm based on the assumption that the two communicating parties have not previously shared a secret key. HMAC is a hash message authentication code that guarantees that the message is not a forgery and actually comes from the authentic source.
43. Which cipher played a significant role in World War II?
- RC4
- Caesar
- Enigma
- One-time pad
Explanation: The Enigma machine was an electromechanical encryption device that created the Enigma cipher and was developed during World War II. The device depended on the distribution of pre-shared keys that were used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
44. One method used by Cryptanalysts to crack codes is based on the fact that some letters of the English language are used more often than others. Which term is used to describe this method?
- cybertext
- meet-in-the-middle
- frequency analysis
- known-plaintext
Explanation: Frequency analysis uses the fact that some characters in the English alphabet are used more often than others. The letters E, T, and A are the most popular letters and J, Q, X, and Z are the least popular.
45. Why are DES keys considered weak keys?
- They are more resource intensive.
- DES weak keys are difficult to manage.
- They produce identical subkeys.
- DES weak keys use very long key sizes.
Explanation: Weak keys, whether part of an existing encryption algorithm or manually generated, reveal regularities in encryption. This creates a shortcut by which a hacker can break the encryption. DES has four keys for which encryption is identical to decryption.
46. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring an object group on an ASA device. Which configuration keyword should be used after the object group name SERVICE1 ?
- ip
- tcp
- udp
- icmp
Explanation: Because this is a service object group, the keyword should indicate which protocol is used. The options are tcp, udp, tcp-udp, icmp, and icmpv6. The subsequent commands indicate that the services in the group are WWW, FTP, and SMTP. Because all of these protocols use TCP, the keyword in the service object group should be tcp .
47. In the implementation of network security, how does the deployment of a Cisco ASA firewall differ from a Cisco IOS router?
- ASA devices use ACLs that are always numbered.
- ASA devices do not support an implicit deny within ACLs.
- ASA devices support interface security levels.
- ASA devices use ACLs configured with a wildcard mask.
Explanation: The differences between ASA devices and Cisco IOS routers include the following:
An ASA device configured with ACLs is configured with a subnet mask.
An ASA device supports interface security levels.
An ASA device configured with an ACL is always named.
ASA devices and Cisco IOS routers are similar in that they both support an implicit deny within an ACL.
48. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring PAT on an ASA device to enable internal workstations to access the Internet. Which configuration command should be used next?
- nat (inside,outside) dynamic NET1
- nat (outside,inside) dynamic NET1
- nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
- nat (outside,inside) dynamic interface
Explanation: The nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface command indicates that inside hosts are overloading the outside address of the mapped interface.
49. What type of network security test uses simulated attacks to determine the feasibility of an attack as well as the possible consequences if the attack occurs?
- penetration testing
- network scanning
- integrity checking
- vulnerability scanning
Explanation: There are many tests that are used by security specialists to assess the status of a system. They include the following:
penetration testing to determine the feasibility of attacks
network scanning to scan for and identify open TCP ports
integrity checking to check for changes that have occurred in the system
vulnerability scanning to detect potential weaknesses in systems
50. What three tasks can a network administrator accomplish with the Nmap and Zenmap security testing tools? (Choose three.)
- operating system fingerprinting
- assessment of Layer 3 protocol support on hosts
- open UDP and TCP port detection
- security event analysis and reporting
- password recovery
- development of IDS signatures
Explanation: Nmap is a low-level network scanner that is available to the public and that has the ability to perform port scanning, to identify open TCP and UDP ports, and which can also perform system identification. It can also be used to identify Layer 3 protocols that are running on a system. Zenmap is the GUI version of Nmap.
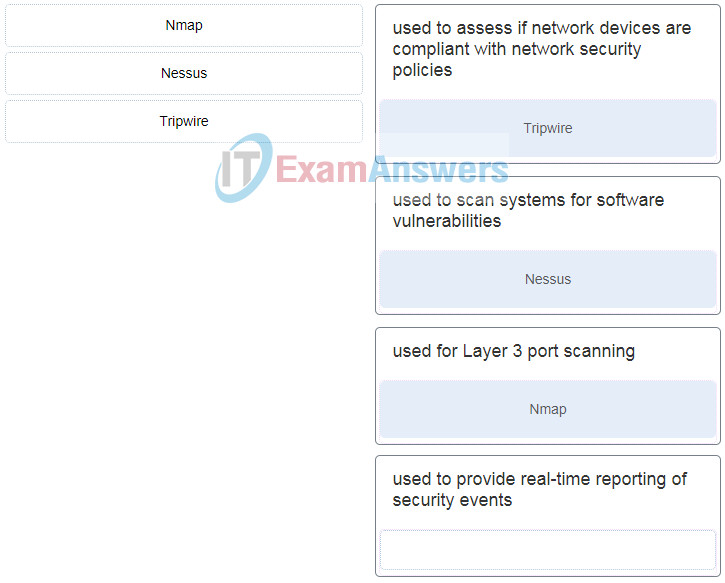
51. Match the network security testing tool with the correct function. (Not all options are used.)
52. Which two means can be used to try to bypass the management of mobile devices? (Choose two.)
- using a fuzzer
- rooting
- jailbreaking
- packet sniffing
- using a Trojan Horse
Explanation: Jailbreaking is a term used when breaking into an Apple iOS device, whereas rooting is the term used for doing the same to an Android device. Both must be concerns in the corporate environment where so many people bring their own devices and access the corporate networks.
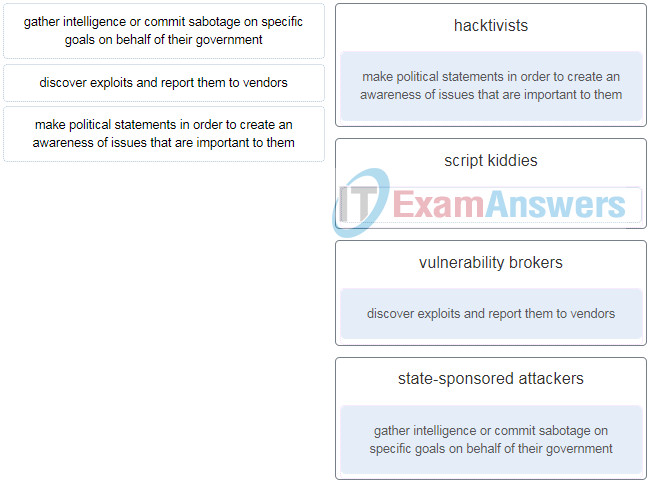
53. Match the type of cyberattackers to the description. (Not all options are used.)
54. What is a benefit of having users or remote employees use a VPN to connect to the existing network rather than growing the network infrastructure?
- security
- scalability
- cost savings
- compatibility
Explanation: A benefit of VPNs is scalability because organizations can use the Internet and easily add new users without adding significant infrastructure. Security is provided by using encryption and authentication protocols to protect data. Another benefit is compatibility because VPNs can be implemented across a wide variety of WAN connections. Organizations also benefit from cost savings because VPNs reduce connectivity costs while simultaneously increasing remote connection bandwidth.
55. What is a difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms?
- Symmetric algorithms are typically hundreds to thousands of times slower than asymmetric algorithms.
- Symmetric encryption algorithms are used to authenticate secure communications. Asymmetric encryption algorithms are used to repudiate messages.
- Symmetric encryption algorithms are used to encrypt data. Asymmetric encryption algorithms are used to decrypt data.
- Symmetric encryption algorithms use pre-shared keys. Asymmetric encryption algorithms use different keys to encrypt and decrypt data.
Explanation: Asymmetric algorithms can use very long key lengths in order to avoid being hacked. This results in the use of significantly increased resources and time compared to symmetric algorithms.
56. What technology allows users to verify the identity of a website and to trust code that is downloaded from the Internet?
- asymmetric key algorithm
- digital signature
- encryption
- hash algorithm
Explanation: Digital signatures provide assurance of the authenticity and integrity of software codes. They provide the ability to trust code that is downloaded from the Internet.
57. Which two statements correctly describe certificate classes used in the PKI? (Choose two.)
- A class 0 certificate is for testing purposes.
- A class 0 certificate is more trusted than a class 1 certificate.
- The lower the class number, the more trusted the certificate.
- A class 5 certificate is for users with a focus on verification of email.
- A class 4 certificate is for online business transactions between companies.
Explanation: A digital certificate class is identified by a number. The higher the number, the more trusted the certificate. The classes include the following:Class 0 is for testing purposes in which no checks have been performed.
Class 1 is for individuals with a focus on verification of email.
Class 2 is for organizations for which proof of identity is required.
Class 3 is for servers and software signing for which independent verification and checking of identity and authority is done by the issuing certificate authority.
Class 4 is for online business transactions between companies.
Class 5 is for private organizations or governmental security.
58. What is the standard for a public key infrastructure to manage digital certificates?
- PKI
- NIST-SP800
- x.503
- x.509
Explanation: The x.509 standard is for a PKI infrastructure and x.500 if for directory structures.
59. Which two statements describe remote access VPNs? (Choose two.)
- Remote access VPNs are used to connect entire networks, such as a branch office to headquarters.
- End users are not aware that VPNs exists.
- A leased line is required to implement remote access VPNs.
- Client software is usually required to be able to access the network.
- Remote access VPNs support the needs of telecommuters and mobile users.
Explanation: Remote access VPNs are designed to provide for the needs of telecommuters and mobile users through the use of software that is installed on the client to encrypt and encapsulate the data. Remote access VPNs can be used across a variety of WAN connections. Users must access the client software to initiate the VPN connection.
60. What are two hashing algorithms used with IPsec AH to guarantee authenticity? (Choose two.)
- MD5
- SHA
- AES
- DH
- RSA
Explanation: The IPsec framework uses various protocols and algorithms to provide data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and secure key exchange. Two popular algorithms used to ensure that data is not intercepted and modified (data integrity and authenticity) are MD5 and SHA.
61. What is the purpose of configuring multiple crypto ACLs when building a VPN connection between remote sites?
- By applying the ACL on a public interface, multiple crypto ACLs can be built to prevent public users from connecting to the VPN-enabled router.
- Multiple crypto ACLs can be configured to deny specific network traffic from crossing a VPN.
- When multiple combinations of IPsec protection are being chosen, multiple crypto ACLs can define different traffic types.
- Multiple crypto ACLs can define multiple remote peers for connecting with a VPN-enabled router across the Internet or network.
Explanation: A crypto ACL can define “interesting traffic” that is used to build a VPN, and forward that “interesting traffic” across the VPN to another VPN-enabled router. Multiple crypto ACLs are used to define multiple different types of traffic and utilize different IPsec protection corresponding to the different types of traffic.
62. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator creates three zones (A, B, and C) in an ASA that filters traffic. Traffic originating from Zone A going to Zone C is denied, and traffic originating from Zone B going to Zone C is denied. What is a possible scenario for Zones A, B, and C?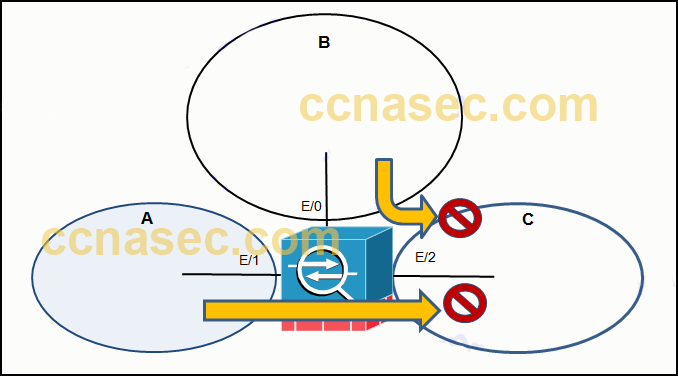
- A – DMZ, B – Inside, C – Outside
- A – Inside, B – DMZ, C – Outside
- A – Outside, B – Inside, C – DMZ
- A – DMZ, B – Outside, C – Inside
Explanation: ASA protects Network/Zone C (Inside) from unauthorized access by users on a Network/Zone B (Outside). It also denies traffic from Network/Zone A (DMZ) to access the Network/Zone C (Inside).
63. What are two monitoring tools that capture network traffic and forward it to network monitoring devices? (Choose two.)
- SIEM
- Wireshark
- SNMP
- SPAN
- network tap
Explanation: A network tap is used to capture traffic for monitoring the network. The tap is typically a passive splitting device implemented inline on the network and forwards all traffic including physical layer errors to an analysis device. SPAN is a port mirroring technology supported on Cisco switches that enables the switch to copy frames and forward them to an analysis device.
64. What is the IPS detection engine that is included in the SEC license for 4000 Series ISRs?
- Security Onion
- Snort
- ASDM
- AMP
Explanation: Snort is the IPS detection and enforcement engine that is included in the SEC license for 4000 Series ISRs.