| How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank. |
|
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
|
CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – Modules 5 – 10: Network Fundamentals Group Exam
1. A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts in the same network
- all hosts on the Internet
- a specially defined group of hosts
2. Which statement describes a characteristic of cloud computing?
- Applications can be accessed over the Internet by individual users or businesses using any device, anywhere in the world.
- Devices can connect to the Internet through existing electrical wiring.
- Investment in new infrastructure is required in order to access the cloud.
- A business can connect directly to the Internet without the use of an ISP.
3. A network administrator can successfully ping the server at www.cisco.com, but cannot ping the company web server located at an ISP in another city. Which tool or command would help identify the specific router where the packet was lost or delayed?
- netstat
- telnet
- ipconfig
- traceroute
4. What type of information is contained in an ARP table?
- domain name to IP address mappings
- switch ports associated with destination MAC addresses
- routes to reach destination networks
- IP address to MAC address mappings
5. Match the characteristic to the protocol category. (Not all options are used.)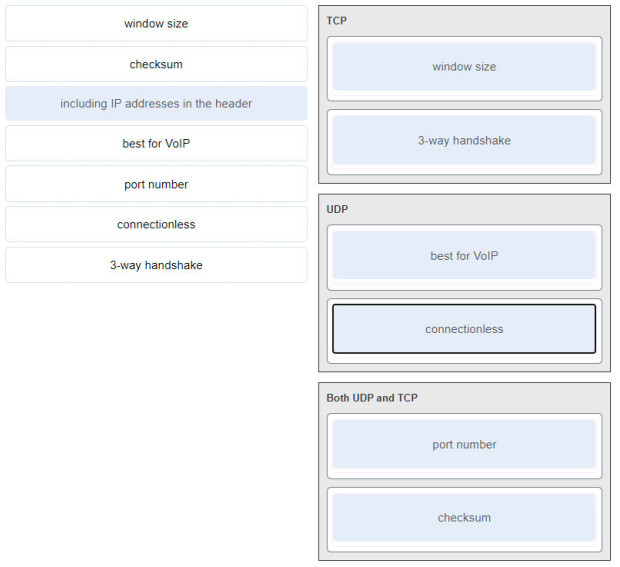
TCP:
- 3-wayhandshake
- window size
UDP:
- connectionless
- best for VoIP
Both UDP and TCP:
- Port number
- checksum
6. When a wireless network in a small office is being set up, which type of IP addressing is typically used on the networked devices?
- private
- public
- network
- wireless
7. Which two parts are components of an IPv4 address? (Choose two.)
- logical portion
- host portion
- broadcast portion
- subnet portion
- network portion
- physical portion
8. Match each IPv4 address to the appropriate address category. (Not all options are used.)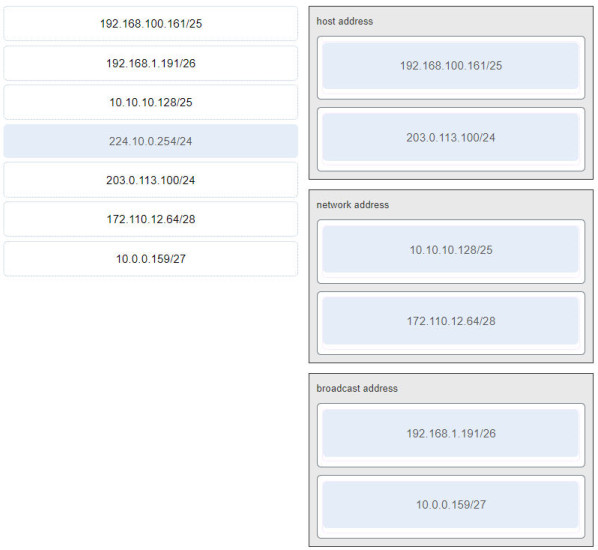
host address:
- 192.168.100.161/25
- 203.0.113.100/24
network address:
- 10.10.10.128/25
- 172.110.12.64/28
broadcast address:
- 192.168.1.191/26
- 10.0.0.159/27
9. A cybersecurity analyst believes an attacker is spoofing the MAC address of the default gateway to perform a man-in-the-middle attack. Which command should the analyst use to view the MAC address a host is using to reach the default gateway?
- route print
- ipconfig /all
- netstat -r
- arp -a
10. A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the network domain of the destination host
- the MAC address of the destination host
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the default gateway
11. What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
12. What type of information is contained in a DNS MX record?
- the IP address of an authoritative name server
- the FQDN of the alias used to identify a service
- the domain name mapped to mail exchange servers
- the IP address for an FQDN entry
13. Match the application protocols to the correct transport protocols.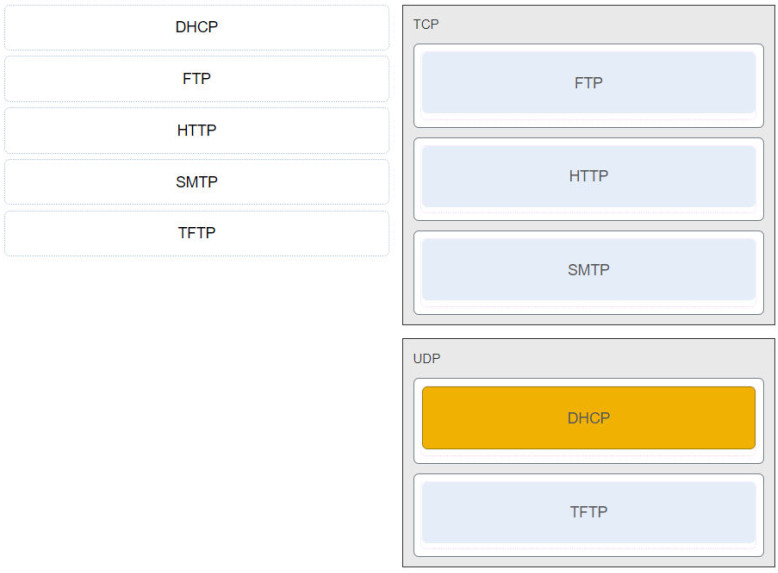
- TCP: FTP, HTTP, SMTP.
- UDP: TFTP, DHCP.
14. A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
- 1000 segments
- 100 segments
- 1 segment
- 10 segments
15. A user issues a ping 192.168.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1 . What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- host unreachable
16. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -r
- show ip route
- netstat -s
- route print
- tracert
route print or netstat -r commands can be used to display the host routing table. Both commands generate the same output. On a router, the show ip route command is used to display the routing table. The netstat -s command is used to display per-protocol statistics. The tracert command is used to display the path that a packet travels to its destination.17. What is the full decompressed form of the IPv6 address 2001:420:59:0:1::a/64?
- 2001:4200:5900:0:1:0:0:a000
- 2001:0420:0059:0000:0001:0000:000a
- 2001:0420:0059:0000:0001:000a
- 2001:0420:0059:0000:0001:0000:0000:000a
- 2001:420:59:0:1:0:0:a
- 2001:4200:5900:0000:1000:0000:0000:a000
18. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2 . What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
0 : net unreachable
1 : host unreachable
2 : protocol unreachable
3 : port unreachable
19. What message informs IPv6 enabled interfaces to use stateful DHCPv6 for obtaining an IPv6 address?
- the ICMPv6 Router Solicitation
- the DHCPv6 Advertise message
- the DHCPv6 Reply message
- the ICMPv6 Router Advertisement
20. Refer to the exhibit. From the perspective of users behind the NAT router, what type of NAT address is 209.165.201.1?
- inside global
- inside local
- outside global
- outside local
21. Match each characteristic to the appropriate email protocol. (Not all options are used.)
POP:
- does not require a centralized backup solution.
- mail is deleted as it is downloaded.
- desirable for an ISP or large business.
IMAP:
- download copies of messages to be the client.
- original messages must be manually deleted.
- requires a larger a mount of disk space.
22. What is done to an IP packet before it is transmitted over the physical medium?
- It is tagged with information guaranteeing reliable delivery.
- It is segmented into smaller individual pieces.
- It is encapsulated in a Layer 2 frame.
- It is encapsulated into a TCP segment.
23. Which PDU is processed when a host computer is de-encapsulating a message at the transport layer of the TCP/IP model?
- segment
- packet
- frame
- bits
14. What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
25. Match the HTTP status code group to the type of message generated by the HTTP server.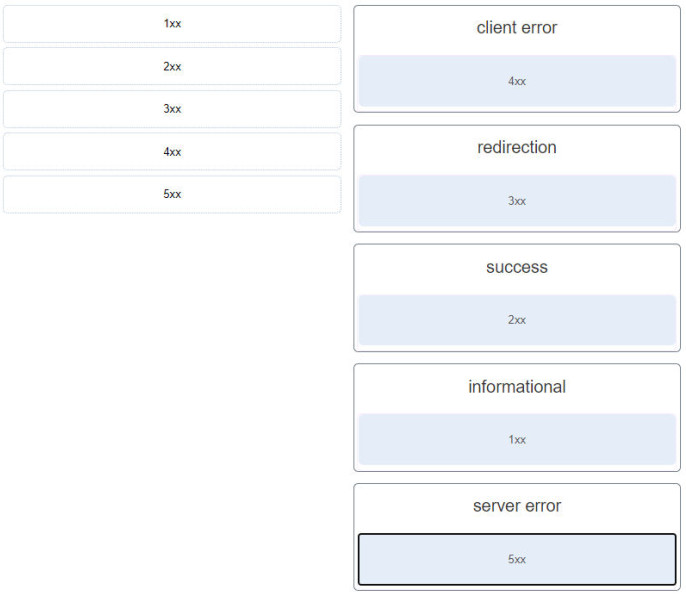
- client error: ~~> 4xx
- redirection: ~~> 3xx
- success: ~~> 2xx
- informational: ~~> 1xx
- server error: ~~> 5xx
26. What network service uses the WHOIS protocol?
- HTTPS
- DNS
- SMTP
- FTP
27. What action does a DHCPv4 client take if it receives more than one DHCPOFFER from multiple DHCP servers?
- It sends a DHCPNAK and begins the DHCP process over again.
- It accepts both DHCPOFFER messages and sends a DHCPACK.
- It discards both offers and sends a new DHCPDISCOVER.
- It sends a DHCPREQUEST that identifies which lease offer the client is accepting.
28. Which networking model is being used when an author uploads one chapter document to a file server of a book publisher?
- peer-to-peer
- client/server
- master-slave
- point-to-point
29. Which protocol is a client/server file sharing protocol and also a request/response protocol?
- FTP
- UDP
- TCP
- SMB
30. How is a DHCPDISCOVER transmitted on a network to reach a DHCP server?
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the broadcast IP address as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with a multicast IP address that all DHCP servers listen to as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the default gateway as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the DHCP server as the destination address.
31. What is a description of a DNS zone transfer?
- transferring blocks of DNS data from a DNS server to another server
- the action taken when a DNS server sends a query on behalf of a DNS resolver
- forwarding a request from a DNS server in a subdomain to an authoritative source
- finding an address match and transferring the numbered address from a DNS server to the original requesting client
32. What are the two sizes (minimum and maximum) of an Ethernet frame? (Choose two.)
- 128 bytes
- 64 bytes
- 1024 bytes
- 56 bytes
- 1518 bytes
33. A user who is unable to connect to the file server contacts the help desk. The helpdesk technician asks the user to ping the IP address of the default gateway that is configured on the workstation. What is the purpose for this ping command?
- to resolve the domain name of the file server to its IP address
- to request that gateway forward the connection request to the file server
- to obtain a dynamic IP address from the server
- to test that the host has the capability to reach hosts on other networks
ping command is used to test connectivity between hosts. The other options describe tasks not performed by ping . Pinging the default gateway will test whether the host has the capability to reach hosts on its own network and on other networks.34. A user gets an IP address of 192.168.0.1 from the company network administrator. A friend of the user at a different company gets the same IP address on another PC. How can two PCs use the same IP address and still reach the Internet, send and receive email, and search the web?
- ISPs use Domain Name Service to change a user IP address into a public IP address that can be used on the Internet.
- Both users must be using the same Internet Service Provider.
- Both users must be on the same network.
- ISPs use Network Address Translation to change a user IP address into an address that can be used on the Internet.
35. How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
- 30
- 32
- 60
- 62
- 64
36. What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 127.16.0.0/12
37. Which process failed if a computer cannot access the internet and received an IP address of 169.254.142.5?
- DNS
- IP
- HTTP
- DHCP
38. Which statement describes a feature of the IP protocol?
- IP relies on Layer 2 protocols for transmission error control.
- MAC addresses are used during the IP packet encapsulation.
- IP relies on upper layer services to handle situations of missing or out-of-order packets.
- IP encapsulation is modified based on network media.
39. What is a basic characteristic of the IP protocol?
- connectionless
- media dependent
- user data segmentation
- reliable end-to-end delivery
40. Which statement describes the ping and tracert commands?
- Both ping and tracert can show results in a graphical display.
- Ping shows whether the transmission is successful; tracert does not.
- Tracert shows each hop, while ping shows a destination reply only.
- Tracert uses IP addresses; ping does not.
41. A large corporation has modified its network to allow users to access network resources from their personal laptops and smart phones. Which networking trend does this describe?
- cloud computing
- video conferencing
- online collaboration
- bring your own device
42. Match each description to its corresponding term. (Not all options are used.)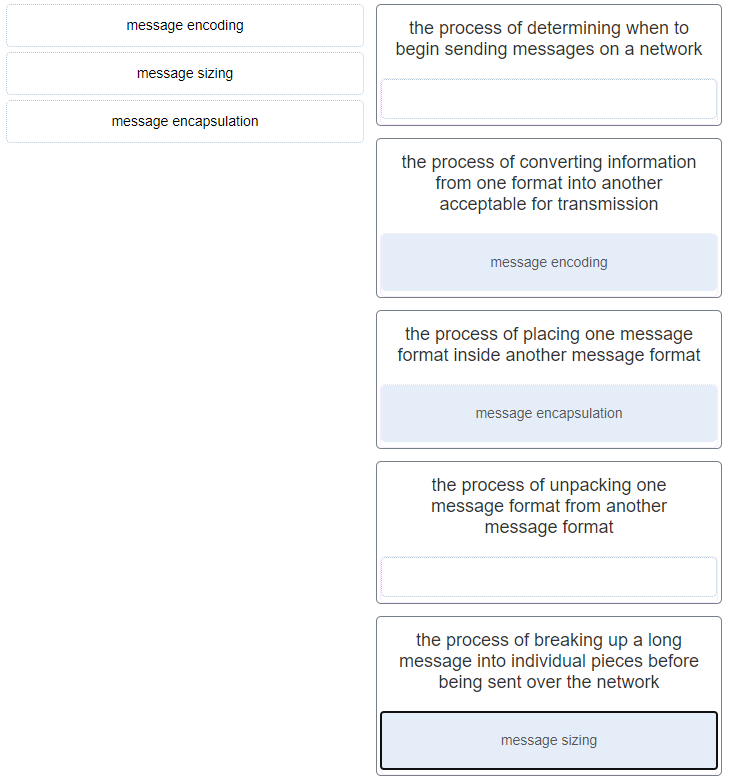
- message encoding : the process of converting information from one format into another acceptable for transmission
- message sizing : the process of breaking up a long message into individual pieces before being sent over the network
- message encapsulation : the process of placing one message format inside another message format
- (Empty) : the process of determining when to begin sending messages on a network
- (Empty) : the process of unpacking one message format from another message format
43. Which method would an IPv6-enabled host using SLAAC employ to learn the address of the default gateway?
- router advertisement messages received from the link router
- router solicitation messages received from the link router
- neighbor advertisement messages received from link neighbors
- neighbor solicitation messages sent to link neighbors
44. Which type of transmission is used to transmit a single video stream such as a web-based video conference to a select number of users?
- anycast
- broadcast
- unicast
- multicast
45. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 attempts to connect to File_server1 and sends an ARP request to obtain a destination MAC address. Which MAC address will PC1 receive in the ARP reply?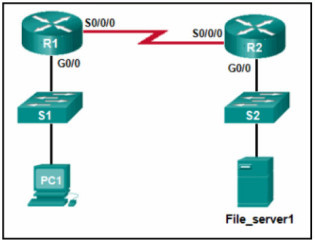
- the MAC address of the GO/O interface on R2
- the MAC address of S2
- the MAC address of S1
- the MAC address of File_server1
- the MAC address of the GO/O interface on R1
46. What is the result of an ARP poisoning attack?
- Network clients are infected with a virus.
- Network clients experience a denial of service.
- Client memory buffers are overwhelmed.
- Client information is stolen.
47. What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
48. Refer to the exhibit. This PC is unable to communicate with the host at 172.16.0.100. What information can be gathered from the displayed output?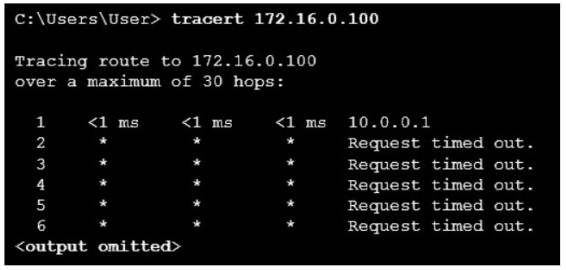
- The target host is turned off.
- The communication fails after the default gateway.
- 172.16.0.100 is only a single hop away.
- This PC has the wrong subnet configured on its NIC
tracert command shows the path a packet takes through the network to the destination. In this example, only a response from the first router in the path is received, and all other responses time out. The first router is the default gateway for this host, and because a response is received from the router, it can be assumed that this host is on the same subnet as the router.49. A user issues a ping 192.168.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- port unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- host unreachable
50. Which two operations are provided by TCP but not by UDP? (Choose two.)
- retransmitting any unacknowledged data
- acknowledging received data
- reconstructing data in the order received
- identifying the applications
- tracking individual conversations
51. A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the RTT value reaches zero
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
52. A network administrator is testing network connectivity by issuing the ping command on a router. Which symbol will be displayed to indicate that a time expired during the wait for an ICMP echo reply message?
- U
- .
- !
- $
ping command is issued on a router, the most common indicators are as follows:! – indicates receipt of an ICMP echo reply message
. – indicates a time expired while waiting for an ICMP echo reply message
U – an ICMP message of unreachability was received
53. A technician is configuring email on a mobile device. The user wants to be able to keep the original email on the server, organize it into folders, and synchronize the folders between the mobile device and the server. Which email protocol should the technician use?
- SMTP
- MIME
- POP3
- IMAP
54. At which OSI layer is a source MAC address added to a PDU during the encapsulation process?
- application layer
- presentation layer
- data link layer
- transport layer
55. Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Time-to-Live
- Fragment Offset
- Header Length
- Differentiated Services
56. What are three responsibilities of the transport layer? (Choose three.)
- identifying the applications and services on the client and server that should handle transmitted data
- conducting error detection of the contents in frames
- meeting the reliability requirements of applications, if any
- directing packets towards the destination network
- formatting data into a compatible form for receipt by the destination devices
- multiplexing multiple communication streams from many users or applications on the same network
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
Multiplexing the communications of multiple users or applications over a single network
Managing the reliability requirements of applications
57. How does network scanning help assess operations security?
- It can detect open TCP ports on network systems.
- It can detect weak or blank passwords.
- It can simulate attacks from malicious sources.
- It can log abnormal activity.
58. Refer to the exhibit. A network security analyst is examining captured data using Wireshark. The captured frames indicate that a host is downloading malware from a server. Which source port is used by the host to request the download?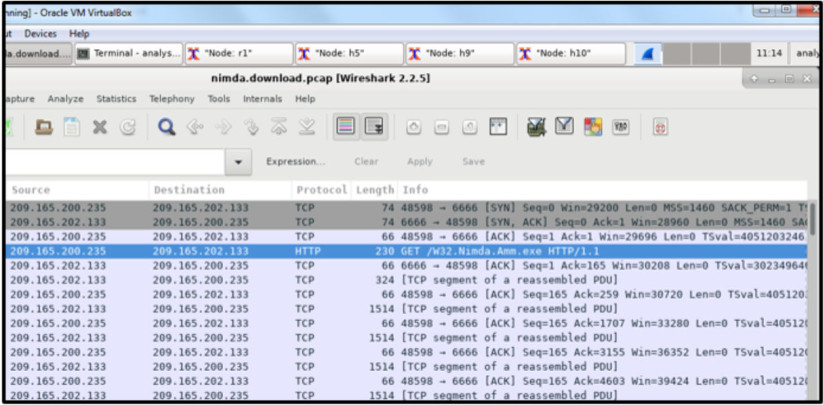
- 66
- 1514
- 6666
- 48598
59. What are three responsibilities of the transport layer? (Choose three.)
- identifying the applications and services on the client and server that should handle transmitted data
- conducting error detection of the contents in frames
- meeting the reliability requirements of applications, if any
- directing packets towards the destination network
- formatting data into a compatible form for receipt by the destination devices
- multiplexing multiple communication streams from many users or applications on the same network
Tracking the individual communication streams between applications on the source and destination hosts
Segmenting data at the source and reassembling the data at the destination
Identifying the proper application for each communication stream through the use of port numbers
Multiplexing the communications of multiple users or applications over a single network
Managing the reliability requirements of applications
60. Which two ICMP messages are used by both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols? (Choose two.)
- route redirection
- neighbor solicitation
- router solicitation
- router advertisement
- protocol unreachable
61. What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
62. A device has been assigned the IPv6 address of 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000:00d8:0058:00ab/64. Which is the host identifier of the device?
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000:00d8:0058:00ab
- 00ab
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500
- 1000:00d8:0058:00ab
63. What three application layer protocols are part of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose three.)
- DHCP
- PPP
- FTP
- DNS
- NAT
- ARP
64. A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
65. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC3. In this scenario, what will happen next?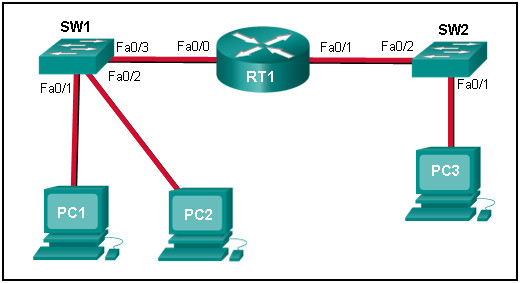
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its own Fa0/1 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC3 MAC address.
- RT1 will forward the ARP request to PC3.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its own Fa0/0 MAC address.