| How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank. |
|
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
|
Network Security ( Version 1) – Network Security 1.0 Modules 11-12: Intrusion Prevention Group Exam Answers
- neither introduce latency or jitter
- both use signatures to detect patterns
- both are deployed inline in the data stream
- both can stop trigger packets
- both can detect atomic patterns
Explanation: IDS sensors work off line and are passive. They add very little latency, however they cannot stop trigger packets. An IPS can stop trigger packets but because they are installed inline they add some latency and jitter to the traffic.
2. What is an advantage of using an IPS?
- It is installed outside of the data traffic flow.
- It does not impact network traffic if there is a sensor overload.
- It can stop trigger packets.
- It has no impact on network latency.
Explanation: An IPS can stop trigger packets but because they are installed inline they add some latency and jitter to the traffic. IDS sensors work off line and are passive. They add very little latency. However they cannot stop trigger packets.
3. What is a characteristic of an IDS?
- It can affect network performance by introducing latency and jitter.
- It often requires assistance from other network devices to respond to an attack.
- It is installed inline with the network traffic flow.
- It can be configured to drop trigger packets that are associated with a connection.
Explanation: An IDS often requires assistance from other networking devices, such as routers and firewalls, to respond to an attack.
4. What are two characteristics of an IPS operating in promiscuous mode? (Choose two.)
- It can stop malicious traffic from reaching the intended target for all types of attacks.
- It sits directly in the path of the traffic flow.
- It requires the assistance of another network device to respond to an attack.
- It does not impact the flow of packets in forwarded traffic.
- It sends alerts and drops any malicious packets.
Explanation: An advantage of an IPS operating in promiscuous mode is that the sensor does not affect the packet flow with the forwarded traffic. A disadvantage is that the sensor cannot stop malicious traffic from reaching its intended target for certain types of attacks, such as atomic attacks (single-packet attacks).
5. Which tool can perform real-time traffic and port analysis, and can also detect port scans, fingerprinting and buffer overflow attacks?
- SIEM
- Nmap
- Snort
- Netflow
Explanation: Snort is an open source intrusion protection system (IPS) that is capable of performing real-time traffic and port analysis, packet logging, content searching and matching, as well as detecting probes, attacks, port scans, fingerprinting, and buffer overflow attacks.
6. Which Snort IPS feature enables a router to download rule sets directly from cisco.com or snort.org?
- Snort rule set pull
- Signature allowed listing
- Snort rule set push
- Snort rule set updates
Explanation: With the Snort rule set pull feature, a router can download rule sets directly from cisco.com or snort.org to a local server. The download can occur using one-time commands or periodic automated updates.
7. What is a minimum system requirement to activate Snort IPS functionality on a Cisco router?
- at least 4 GB RAM
- at least 4 GB flash
- ISR 2900 or higher
- K9 license
Explanation: The requirements to run Snort IPS include ISR 4300 or higher, K9 license, 8 GB RAM, and 8 GB flash.
8. What is PulledPork?
- an open source network IPS that performs real-time traffic analysis and generates alerts when threats are detected on IP networks
- a centralized management tool to push the rule sets based on preconfigured policy, to Cisco routers
- a virtual service container that runs on the Cisco ISR router operating system
- a rule management application that can be used to automatically download Snort rule updates
Explanation: PulledPork is a rule management application that can be used to automatically download Snort rule updates. Using PulledPork requires an authorization code, called an oinkcode, obtained from a snort.org account.
9. What are two actions that an IPS can perform whenever a signature detects the activity for which it is configured? (Choose two.)
- disable the link
- reconverge the network
- drop or prevent the activity
- allow the activity
- restart the infected device
Explanation: Depending on the signature type and the platform, whenever a signature detects the activity for which it is configured the IPS may:
log the activity
drop or prevent the activity
reset a TCP connection
block future activity
allow the activity
10. Which IPS signature trigger category uses a decoy server to divert attacks away from production devices?
- honey pot-based detection
- policy-based detection
- pattern-based detection
- anomaly-based detection
Explanation: Honey pot-based detection uses a decoy server to attract attacks and to divert attacks away from production devices. Use of a honey pot can give administrators time to analyze incoming attacks and malicious traffic patterns to tune sensor signatures.
11. What situation will generate a true negative IPS alarm type?
- normal traffic that generates a false alarm
- a verified security incident that is detected
- a known attack that is not detected
- normal traffic that is correctly being ignored and forwarded
Explanation: The true negative alarm type is used when normal network traffic flows through an interface. Normal traffic should not, and does not generate an actual alarm. A true negative indicates that benign normal traffic is correctly being ignored and forwarded without generating an alert.
12. Match each intrusion protection service with the description.
13. Match each Snort IPS rule action with the description.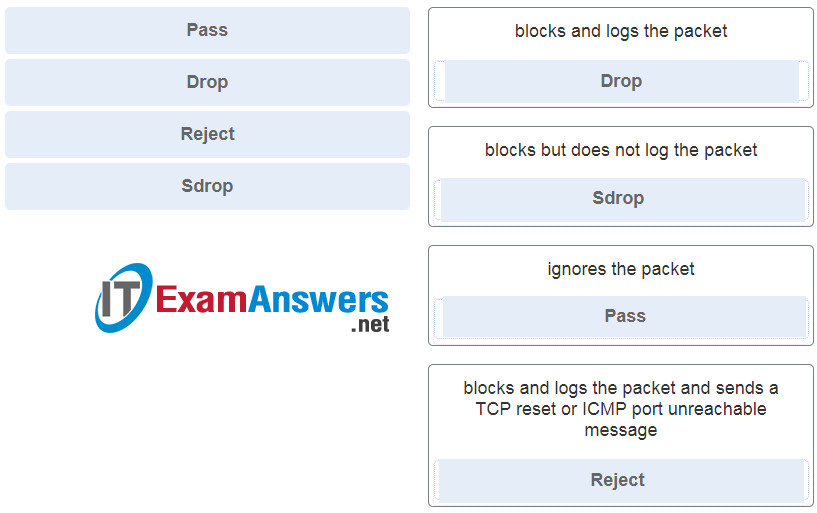
14. What is provided by the fail open and close functionality of Snort IPS?
- provides the ability to automatically disable problematic signatures that routinely cause false positives and pass traffic
- blocks the traffic flow or bypasses IPS checking in the event of an IPS engine failure
- keeps Snort current with the latest threat protection and term-based subscriptions
- keeps track of the health of the Snort engine that is running in the service container
Explanation: The Snort IPS fail open and close functionality can be configured to block the traffic flow or to bypass IPS checking in the event of IPS engine failure.
15. What is a characteristic of the Community Rule Set type of Snort term-based subscriptions?
- it has 60-day delayed access to updated signatures
- it uses Cisco Talos to provide coverage in advance of exploits
- it is fully supported by Cisco
- it is available for free
Explanation: There are two types of Snort term-based subscriptions:
Community Rule Set – Available for free and provides limited coverage against threats. There is also a 30-day delayed access to updated signatures and there is no Cisco customer support available.
Subscriber Rule Set – Available for a fee and provides the best protection against threats. It includes coverage in advance of exploits by using the research work of the Cisco Talos security experts. This subscription is fully supported by Cisco.
16. What is a characteristic of the connectivity policy setting when configuring Snort threat protection?
- it attempts to balance network security with network performance
- it prioritizes security over connectivity
- it provides the lowest level of protection
- it enables the highest number of signatures to be verified
Explanation: One of the functionalities of Snort IPS is that it provides three levels of signature protection.
Connectivity – The least secure option.
Balanced – The mid-range option of security.
Security – The most secure option.
17. What is contained in an OVA file?
- a current compilation of known threats and prevention mechanisms
- an installable version of a virtual machine
- a list of atomic and composite signatures
- a set of rules for an IDS or IPS to detect intrusion activity
Explanation: Step 1 of the configuration of Snort IPS is to download an Open Virtualization Archive (OVA) file. This file contains a compressed, installable version of a virtual machine.
18. What is a network tap?
- a Cisco technology that provides statistics on packets flowing through a router or multilayer switch
- a technology used to provide real-time reporting and long-term analysis of security events
- a feature supported on Cisco switches that enables the switch to copy frames and forward them to an analysis device
- a passive device that forwards all traffic and physical layer errors to an analysis device
Explanation: A network tap is used to capture traffic for monitoring the network. The tap is typically a passive splitting device implemented inline on the network and forwards all traffic, including physical layer errors, to an analysis device.
19. Which statement describes the function of the SPAN tool used in a Cisco switch?
- It is a secure channel for a switch to send logging to a syslog server.
- It provides interconnection between VLANs over multiple switches.
- It supports the SNMP trap operation on a switch.
- It copies the traffic from one switch port and sends it to another switch port that is connected to a monitoring device.
Explanation: To analyze network traffic passing through a switch, switched port analyzer (SPAN) can be used. SPAN can send a copy of traffic from one port to another port on the same switch where a network analyzer or monitoring device is connected. SPAN is not required for syslog or SNMP. SPAN is used to mirror traffic, while syslog and SNMP are configured to send data directly to the appropriate server.
20. A network administrator is trying to download a valid file from an internal server. However, the process triggers an alert on a NMS tool. What condition describes this alert?
- false negative
- false positive
- true negative
- true positive
Explanation: Alerts can be classified as follows:
True Positive: The alert has been verified to be an actual security incident.
False Positive: The alert does not indicate an actual security incident. Benign activity that results in a false positive is sometimes referred to as a benign trigger.
An alternative situation is that an alert was not generated. The absence of an alert can be classified as:
True Negative: No security incident has occurred. The activity is benign.
False Negative: An undetected incident has occurred.
21. What is an advantage of HIPS that is not provided by IDS?
- HIPS provides quick analysis of events through detailed logging.
- HIPS deploys sensors at network entry points and protects critical network segments.
- HIPS monitors network processes and protects critical files.
- HIPS protects critical system resources and monitors operating system processes.
Explanation: Network-based IDS (NIDS) sensors are typically deployed in offline mode. They do not protect individual hosts. Host-based IPS (HIPS) is software installed on a single host to monitor and analyze suspicious activity. It can monitor and protect operating system and critical system processes that are specific to that host. HIPS can be thought of as a combination of antivirus software, antimalware software, and a firewall.
22. What information must an IPS track in order to detect attacks matching a composite signature?
- the total number of packets in the attack
- the state of packets related to the attack
- the attacking period used by the attacker
- the network bandwidth consumed by all packets
Explanation: A composite signature is called a stateful signature. It identifies a sequence of operations distributed across multiple hosts over an arbitrary period of time. Because this type of attack involves multiple packets, an IPS sensor must maintain the state information. However, an IPS sensor cannot maintain the state information indefinitely. A composite signature is configured with a time period to maintain the state for the specific attack when it is first detected. Thus, an IPS may not be able to maintain all the information related to an attack such as total number of packets, total length of attack time, and the amount of bandwidth consumed by the attack.