| How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank. |
|
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
|
Network Security (Version 1.0) Modules 13 – 14: Layer 2 and Endpoint Security Group Exam Answers
1. Why are traditional network security perimeters not suitable for the latest consumer-based network endpoint devices?
- These devices are not managed by the corporate IT department.
- These devices pose no risk to security as they are not directly connected to the corporate network.
- These devices connect to the corporate network through public wireless networks.
- These devices are more varied in type and are portable.
Explanation: Traditional network security has two major focuses: (1) end point protection using antivirus software and enabling the personal firewall, and (2) network border protection with firewalls, proxy servers, and network packet scanning devices or software. This type of protection is not suited for the new network devices that are mobile, frequently access cloud storage, and may be a personal device.
2. What two internal LAN elements need to be secured? (Choose two.)
- edge routers
- IP phones
- fiber connections
- switches
- cloud-based hosts
Explanation: Internal network protection is just as important as securing the network perimeter. Internal LAN elements can be broken up into endpoints and network infrastructure devices. Common endpoints include laptops, desktops, servers, and IP phones. LAN infrastructure devices include switches and access points.
3. What are two examples of traditional host-based security measures? (Choose two.)
- host-based IPS
- NAS
- 802.1X
- antimalware software
- host-based NAC
Explanation: Traditional host-based security measures include antivirus/antimalware software, host-based IPS, and host-based firewall. Antivirus and antimalware software detects and mitigates viruses and malware. A host-based IPS is used to monitor and report on the system configuration and application activity, security events, policy enforcement, alerting, and rootkit detection. A host-based firewall restricts incoming and outgoing connections for a particular host.
4. In an 802.1x deployment, which device is a supplicant?
- RADIUS server
- access point
- switch
- end-user station
Explanation: In 802.1x, a supplicant is the end-user device (such as a laptop) that is attempting to attach to the WLAN.
5. A company implements 802.1X security on the corporate network. A PC is attached to the network but has not authenticated yet. Which 802.1X state is associated with this PC?
- err-disabled
- disabled
- unauthorized
- forwarding
Explanation: When a port is configured for 802.1X, the port starts in the unauthorized state and stays that way until the client has successfully authenticated.
6. An 802.1X client must authenticate before being allowed to pass data traffic onto the network. During the authentication process, between which two devices is the EAP data encapsulated into EAPOL frames? (Choose two.)
- data nonrepudiation server
- authentication server (TACACS)
- supplicant (client)
- authenticator (switch)
- ASA Firewall
Explanation: When a client supplicant is starting the 802.1X message exchange, an EAPOL-Start message is sent between the supplicant and the authenticator, which is the switch. EAP data between the supplicant and the authenticator is encapsulated in EAPOL frames.
7. Which command is used as part of the 802.1X configuration to designate the authentication method that will be used?
- dot1x system-auth-control
- aaa authentication dot1x
- aaa new-model
- dot1x pae authenticator
Explanation: The aaa authentication dot1x default group radius command specifies that RADIUS is used as the method for 802.1X port-based authentication.
8. What is involved in an IP address spoofing attack?
- A rogue node replies to an ARP request with its own MAC address indicated for the target IP address.
- Bogus DHCPDISCOVER messages are sent to consume all the available IP addresses on a DHCP server.
- A rogue DHCP server provides false IP configuration parameters to legitimate DHCP clients.
- A legitimate network IP address is hijacked by a rogue node.
Explanation: In an IP address spoofing attack, the IP address of a legitimate network host is hijacked and used by a rogue node. This allows the rogue node to pose as a valid node on the network.
9. At which layer of the OSI model does Spanning Tree Protocol operate?
- Layer 1
- Layer 2
- Layer 3
- Layer 4
Explanation: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 technology for preventing Layer 2 loops between redundant switch paths.
10. A network administrator uses the spanning-tree loopguard default global configuration command to enable Loop Guard on switches. What components in a LAN are protected with Loop Guard?
- All Root Guard enabled ports.
- All PortFast enabled ports.
- All point-to-point links between switches.
- All BPDU Guard enabled ports.
Explanation: Loop Guard can be enabled globally using the spanning-tree loopguard default global configuration command. This enables Loop Guard on all point-to-point links.
11. Which procedure is recommended to mitigate the chances of ARP spoofing?
- Enable DHCP snooping on selected VLANs.
- Enable IP Source Guard on trusted ports.
- Enable DAI on the management VLAN.
- Enable port security globally.
Explanation: To mitigate the chances of ARP spoofing, these procedures are recommended:
– Implement protection against DHCP spoofing by enabling DHCP snooping globally.
– Enable DHCP snooping on selected VLANs.
– Enable DAI on selected VLANs.
– Configure trusted interfaces for DHCP snooping and ARP inspection. Untrusted ports are configured by default.
12. Which two ports can send and receive Layer 2 traffic from a community port on a PVLAN? (Choose two.)
- community ports belonging to other communities
- promiscuous ports
- isolated ports within the same community
- PVLAN edge protected ports
- community ports belonging to the same community
Explanation: Community ports can send and receive information with ports within the same community, or with a promiscuous port. Isolated ports can only communicate with promiscuous ports. Promiscuous ports can talk to all interfaces. PVLAN edge protected ports only forward traffic through a Layer 3 device to other protected ports.
13. Which protocol should be used to mitigate the vulnerability of using Telnet to remotely manage network devices?
- SNMP
- TFTP
- SSH
- SCP
Explanation: Telnet uses plain text to communicate in a network. The username and password can be captured if the data transmission is intercepted. SSH encrypts data communications between two network devices. TFTP and SCP are used for file transfer over the network. SNMP is used in network management solutions.
14. How can DHCP spoofing attacks be mitigated?
- by disabling DTP negotiations on nontrunking ports
- by implementing port security
- by the application of the ip verify source command to untrusted ports
- by implementing DHCP snooping on trusted ports
Explanation: One of the procedures to prevent a VLAN hopping attack is to disable DTP (auto trunking) negotiations on nontrunking ports. DHCP spoofing attacks can be mitigated by using DHCP snooping on trusted ports. The ip verify source interface configuration command is used to enable IP Source Guard on untrusted ports to protect against MAC and IP address spoofing.
15. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is configuring the port security feature on switch SWC. The administrator issued the command show port-security interface fa 0/2 to verify the configuration. What can be concluded from the output that is shown? (Choose three.)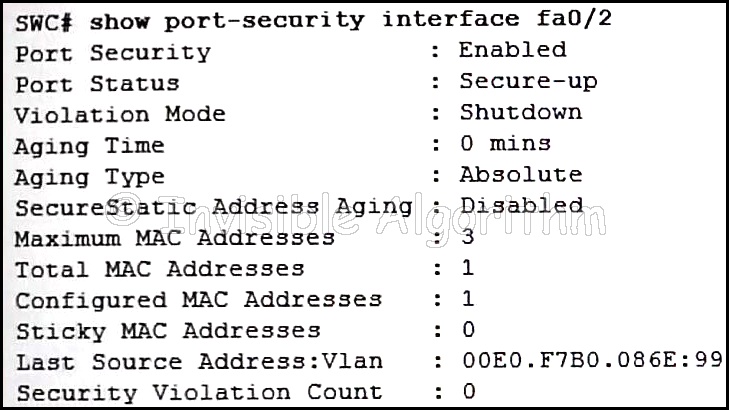
- Three security violations have been detected on this interface.
- This port is currently up.
- The port is configured as a trunk link.
- Security violations will cause this port to shut down immediately.
- There is no device currently connected to this port.
- The switch port mode for this interface is access mode.
Explanation: Because the security violation count is at 0, no violation has occurred. The system shows that 3 MAC addresses are allowed on port fa0/2, but only one has been configured and no sticky MAC addresses have been learned. The port is up because of the port status of secure-up. The violation mode is what happens when an unauthorized device is attached to the port. A port must be in access mode in order to activate and use port security.
16. Two devices that are connected to the same switch need to be totally isolated from one another. Which Cisco switch security feature will provide this isolation?
- PVLAN Edge
- DTP
- SPAN
- BPDU guard
Explanation: The PVLAN Edge feature does not allow one device to see traffic that is generated by another device. Ports configured with the PVLAN Edge feature are also known as protected ports. BPDU guard prevents unauthorized connectivity to a wired Layer 2 switch. SPAN is port mirroring to capture data from one port or VLAN and send that data to another port. DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol) is automatically enabled on some switch models to create a trunk if the attached device is configured for trunking. Cisco recommends disabling DTP as a best practice.
17. What is the behavior of a switch as a result of a successful CAM table attack?
- The switch will drop all received frames.
- The switch interfaces will transition to the error-disabled state.
- The switch will forward all received frames to all other ports.
- The switch will shut down.
Explanation: As a result of a CAM table attack, a switch can run out of memory resources to store MAC addresses. When this happens, no new MAC addresses can be added to the CAM table and the switch will forward all received frames to all other ports. This would allow an attacker to capture all traffic that is flooded by the switch.
18. Which protocol defines port-based authentication to restrict unauthorized hosts from connecting to the LAN through publicly accessible switch ports?
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- 802.1x
- SSH
Explanation: 802.1x is an IEEE standard that defines port-based access control. By authenticating each client that attempts to connect to the LAN, 802.1x provides protection from unauthorized clients.
19. What device is considered a supplicant during the 802.1X authentication process?
- the router that is serving as the default gateway
- the authentication server that is performing client authentication
- the client that is requesting authentication
- the switch that is controlling network access
Explanation: The devices involved in the 802.1X authentication process are as follows:
- The supplicant, which is the client that is requesting network access
- The authenticator, which is the switch that the client is connecting to and that is actually controlling physical network access
- The authentication server, which performs the actual authentication
20. Which term describes the role of a Cisco switch in the 802.1X port-based access control?
- agent
- supplicant
- authenticator
- authentication server
Explanation: 802.1X port-based authentication defines specific roles for the devices in the network:
Client (Supplicant) – The device that requests access to LAN and switch services
Switch (Authenticator) – Controls physical access to the network based on the authentication status of the client
Authentication server – Performs the actual authentication of the client
21. What type of data does the DLP feature of Cisco Email Security Appliance scan in order to prevent customer data from being leaked outside of the company?
- inbound messages
- outbound messages
- messages stored on a client device
- messages stored on the email server
Explanation: Cisco ESAs control outbound messages through data-loss prevention (DLP), email encryption, and optional integration with the RSA Enterprise Manager. This control helps ensure that the outbound messages comply with industry standards and are protected in transit.
22. What is the goal of the Cisco NAC framework and the Cisco NAC appliance?
- to ensure that only hosts that are authenticated and have had their security posture examined and approved are permitted onto the network
- to monitor data from the company to the ISP in order to build a real-time database of current spam threats from both internal and external sources
- to provide anti-malware scanning at the network perimeter for both authenticated and non-authenticated devices
- to provide protection against a wide variety of web-based threats, including adware, phishing attacks, Trojan horses, and worms
Explanation: The NAC framework uses the Cisco network infrastructure and third-party software to ensure the wired and wireless endpoints that want to gain access to the network adheres to the requirements defined by the security policy. The Cisco NAC Appliance is the device that enforces security policy compliance.
23. Which Cisco solution helps prevent MAC and IP address spoofing attacks?
- Port Security
- DHCP Snooping
- IP Source Guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
Explanation: Cisco provides solutions to help mitigate Layer 2 attacks including:
- IP Source Guard (IPSG) – prevents MAC and IP address spoofing attacks
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) – prevents ARP spoofing and ARP poisoning attacks
- DHCP Snooping – prevents DHCP starvation and SHCP spoofing attacks
- Port Security – prevents many types of attacks including MAC table overflow attacks and DHCP starvation attacks
24. What Layer 2 attack is mitigated by disabling Dynamic Trunking Protocol?
- VLAN hopping
- DHCP spoofing
- ARP poisoning
- ARP spoofing
Explanation: Mitigating a VLAN hopping attack can be done by disabling Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) and by setting the native VLAN of trunk links to VLANs not in use.
25. What is the result of a DHCP starvation attack?
- Legitimate clients are unable to lease IP addresses.
- Clients receive IP address assignments from a rogue DHCP server.
- The attacker provides incorrect DNS and default gateway information to clients.
- The IP addresses assigned to legitimate clients are hijacked.
Explanation: DCHP starvation attacks are launched by an attacker with the intent to create a DoS for DHCP clients. To accomplish this goal, the attacker uses a tool that sends many DHCPDISCOVER messages to lease the entire pool of available IP addresses, thus denying them to legitimate hosts.
26. A network administrator is configuring DAI on a switch with the command ip arp inspection validate dst-mac . What is the purpose of this configuration command?
- to check the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table
- to check the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs
- to check the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body
- to check the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header against the source MAC address in the ARP body
Explanation: DAI can be configured to check for both destination or source MAC and IP addresses:
Destination MAC – Checks the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
Source MAC – Checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
IP address – Checks the ARP body for invalid and unexpected IP addresses including addresses 0.0.0.0, 255.255.255.255, and all IP multicast addresses.